Outbound Workers
Outbound Workers sit between your customer’s Workers and the public Internet. They give you visibility into all outgoing fetch() requests from User Workers.
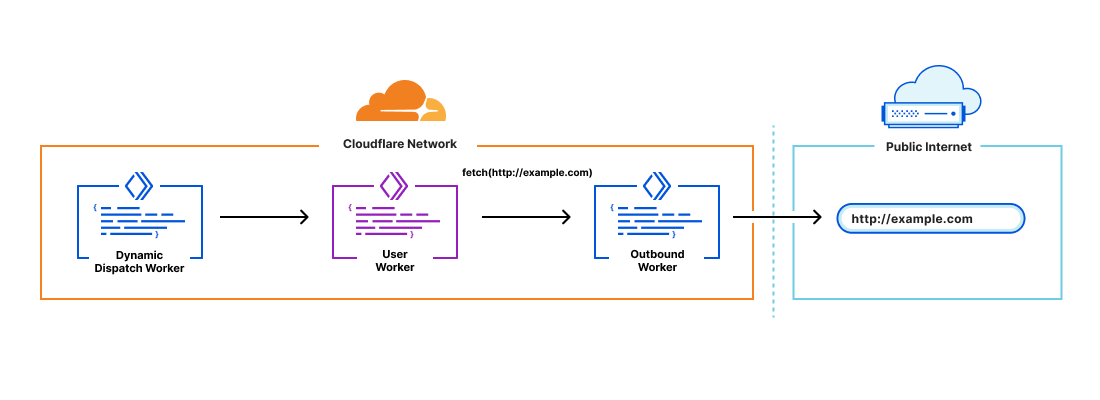
General Use Cases
Outbound Workers can be used to:
- Log all subrequests to identify malicious hosts or usage patterns.
- Create, allow, or block lists for hostnames requested by user Workers.
- Configure authentication to your APIs behind the scenes (without end developers needing to set credentials).
Use Outbound Workers
To use Outbound Workers:
- Create a Worker intended to serve as your Outbound Worker.
- Outbound Worker can be specified as an optional parameter in the dispatch namespaces binding in a projects wrangler.toml. Optionally, to pass data from your Dispatch Worker to the Outbound Worker, the variable names must be specified under parameters.
Make sure that you have wrangler@3.3.0 or later installed.
wrangler.toml[[dispatch_namespaces]]
binding = "dispatcher"
namespace = "<NAMESPACE_NAME>"
outbound = {service = "<SERVICE_NAME>", parameters = [customer_name,url]}
- Edit your Dispatch Worker to call the Outbound Worker and declare variables to pass on
dispatcher.get().
index.jsexport default { async fetch(request, env) { try { // parse the URL, read the subdomain let workerName = new URL(request.url).host.split('.')[0]; let userWorker = env.dispatcher.get( workerName, {}, {// outbound arguments outbound: { customer_name: workerName, url: request.url} } } ); return await userWorker.fetch(request); } catch (e) { if (e.message.startsWith('Worker not found')) { // we tried to get a worker that doesn't exist in our dispatch namespace return new Response('', { status: 404 }); } return new Response(e.message, { status: 500 }); } },
};
- The Outbound Worker will now be invoked on any
fetch()requests from user Workers. The User Worker will trigger a FetchEvent on the Outbound Worker. The variables declared in the binding can be accessed in the Outbound Worker throughenv.<VAR_NAME>.